VISION
Vision
Nurturing Leadership-Level Professionals Practical Education
T
Transdisciplinary Education
Goal 1
-
― Boot camp
-
― APR familiarization & Intensive Course
-
― Communication and Presentation
-
― Systems engineering
-
― Multi-discipline electives
P
Practical Education
Goal 2
-
― Project based courses
-
― Team teaching by academic and practical professors
-
― KINGS Specialization Programs
-
― Systems engineering
-
― Field trip and outdoor activities
N
Nurturing Leadership Level Professional
Goal 3
-
― Technical Writing
-
― Colloquium
-
― Global Leadership Program
-
― Internship Program
-
― Cross Cultural Program
I
Innovative Education Program
Goal 4
-
― Small modular reactor
-
― Desalination cogeneration power plant
-
― Load following
-
― Smart grid
-
― Demand control
Strategies
-
1. Providing multidisciplinary courses : thermodynamics, nuclear safety analysis, reactor physics, mechanical engineering, civil structural engineering, electrical engineering,I&C engineering, radiation protection, radioactive waste management, engineering management, project management, public acceptance, and stakeholder involvement.
-
2. Using a transdisciplinary approach in handling NPP life-cycle activities: pre-project and project decision - making, plant construction, plant operation, and plant decommissioning.
-
3. Integrating life cycle considerations, systems approach, practical capability, international communication and collaboration.
-
4. Applying systems engineering management processes to Korean standard nuclear power plant technology and administration.
-
5. Focusing specifically on nuclear power plant engineering and management.
-
6. Integrating total engineering efforts to meet cost, schedule, and technical performance objectives.
-
1. Combining education and research.
-
2. Synthesizing theoretical and experiential knowledge.
-
3. Harmonizing technology and management expertise.
-
4. Integrating and optimizing lifecycle concerns.
-
5. Integrating theoretical study with practical training in technology and management.
-
6. Project-based learning focused on problem-solving capability.
-
Technology Expert Program(TEP) : focus on obtaining integral capability in holistic areas of design-construction-operation-maintenance of NPP systems and discipline engineering interfaces using reverse engineering /re-engineering methods.
-
Systems Engineer Program(SEP) : focus on technology trend analysis, systems engineering management and efficiency enhancement of design, manufacture, construction and O&M of NPP systems and components.
-
Project Engineer Program(PEP) : focus on management engineering based project management and nuclear policy development, planning and integration of NPP project development.
-
1. To train and educate leadership-level practical professionals for international nuclear power establishment
-
2. To cultivate quality-approaches in engineering education with innovative Master degree programs
-
3. Emphasize the capabilities to define needs, design system, control design processes, and analyze & evaluate product design
-
4. Strengthen teamwork, communication, creativity, leadership, entrepreneurial thinking, ethical reasoning, and global contextual analysis
-
5. Operating classes with multinational composite teams
-
6. Nurture internationally competent nuclear professionals equipped with sense of globalization
-
1. The Master of Engineering (M.E.)degree is generally a professional degree offered as a course work-based alternative to the traditional research-based Master of Science(M.S.) degree.
In KINGS, M.E. students should take coursework in the first year and project base specialization programs in the 2nd year. Finally they should submit an individual project report to get a Master of Engineering degree. -
2. The Doctor of Technology (D.Tech.) degree is conferred upon candidates after having completed a course of study in technology, and a project of lengthy duration in a technologically related field.
The degree focuses on developing practical solutions in the workplace, critical analysis, synthesis, and innovation.
Goal 1
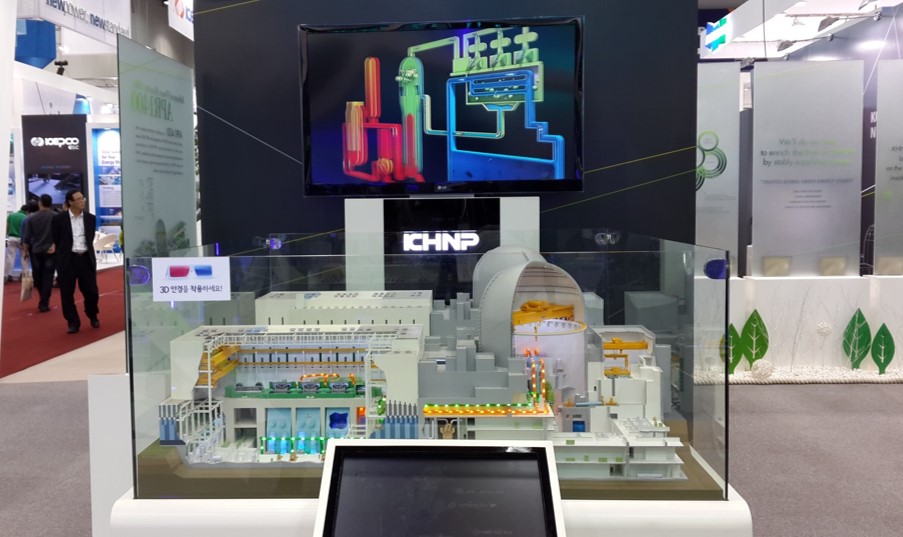

- Practical R&D for Nuclear Industries
- ― Development of R&D projects in the Industry-Academy cooperation (related to nuclear power plant)
- ― Promotion of technology transfer through various projects using the research of Industry-Academy Cooperation
Strategies
- 1Accomplishing the vision of becoming the world best international hub for nuclear power technology. The R&D Foundation of KINGS is founded to effectively establish the Industry-Academy cooperation and to support the research project activities based on the KINGS human resources and research facilities while having the close domestic and international cooperation of Industry-Academy.
- 2Developing and establishing a strong basis of creative R&D for green energy and green growth.
- 3Planning Industry-Academy cooperative R&D.
- 4Contracting, implementing and managing research projects.
- 5Executing KINGS own research projects and managing the R&D internal and external research funds.
- 6Managing technology transfer, intellectual property and patents.
Goal 2

- Systems Engineering Approach to Nuclear Power Plant Engineering
Strategies
- 1Introducing systems engineering to nuclear power plant industries through education and training programs and applying systems engineering to nuclear power plant installations through research activities.
- 2Providing in-depth technical assistance pertaining to the design and operations of complex systems such as nuclear power plants, including hardware, software, and human elements.
- 3Evolving and verifying an integrated, life-cycle balanced set of system solutions that satisfy customer needs.
- 4Integrating three major activities:
- - Development phasing that controls the design process and provides baselines to coordinate design efforts.
- - A systems engineering process that provides a structure for solving design problems and tracking requirements flow throughout the design effort.
- - Life-cycle integration that involves customers in the design process and ensures that the system developed is viable throughout its life.
Goal 3
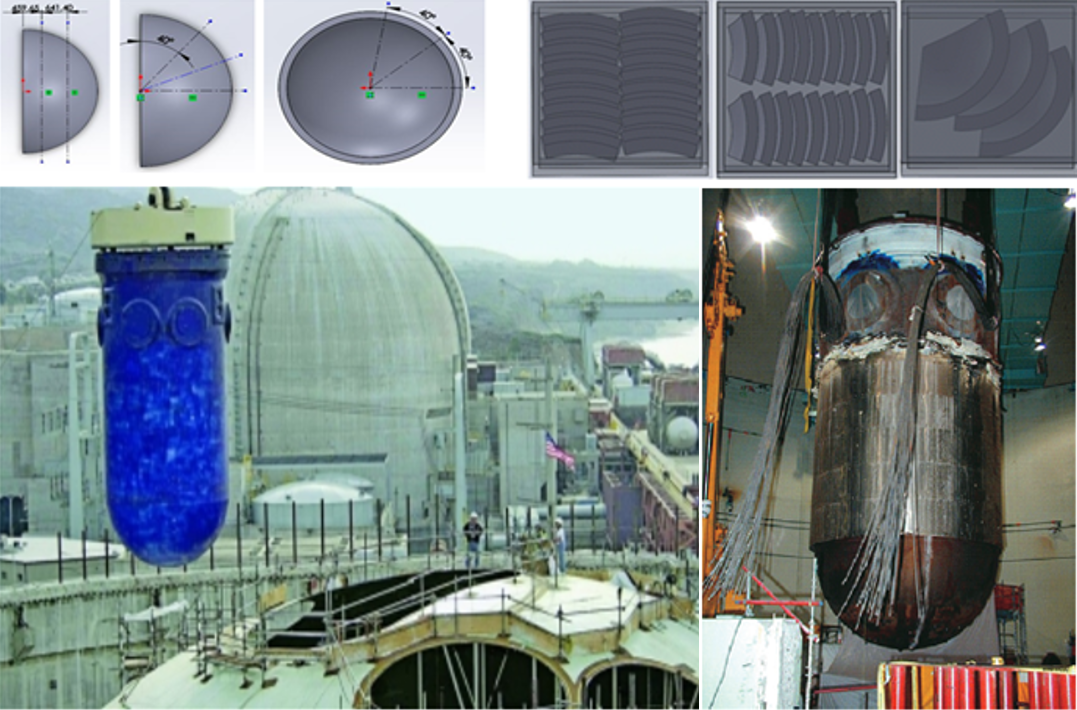

- Radioactive Waste Management and Decommissioning Research Center
- ― Study of radioactive waste management including radioactive waste treatment, packaging, transportation and disposal
- ― Study of NPP decommissioning
- ― Study of back-end nuclear fuel cycle
- ― On-going activities
Strategies
- 1Nuclear Safety Research Center on regulatory technology for NPP decommissioning, decontamination and site remediation (July 2013-April 2018)
- - Developing regulatory technology on NPP decommissioning and site remediation as well as providing technological supports
- - Environment impact assessment of NPP decommissioning
- - Strategy study on decommissioning waste management
- - Packaging and treatment of large components such as reactor pressure vessel and internals
- - Waste minimization and classification, etc.
- 2Source term assessment on decommissioned NPPs
- - Activation source term analysis of Wolsung Unit 1 (June 2013 - May 2016)
- 3Evolving and verifying an integrated, life-cycle balanced set of system solutions that satisfy customer needs.
- 4Integrating three major activities:
- - Development phasing that controls the design process and provides baselines to coordinate design efforts.
- - A systems engineering process that provides a structure for solving design problems and tracking requirements flow throughout the design effort.
- - Life-cycle integration that involves customers in the design process and ensures that the system developed is viable throughout its life.
Goal 4
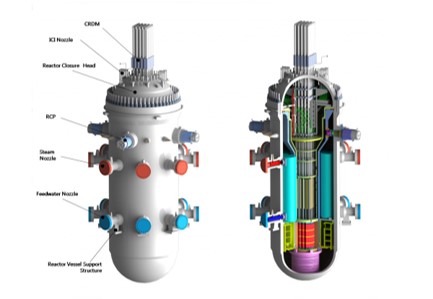
- Green & Smart Energy City Research Center
- ― Small modular reactor
- ― Desalination cogeneration power plant
- ― Load following
- ― Smart grid
- ― Demand control
Strategies
- 1Research on the potential SMR designs and technologies providing much benefits; economic benefit, grid demand smoothing, dedicated fuel cycle management, supply chain advantages, enhanced safety and more flexible siting.
- 2Study on the coupling of SMR with desalination to perform efficient load following.
- 3Develop a small modular reactor which is well suited for integration with renewables through several design features related to the nuclear steam supply system, the power conversion system, and the overall plant architecture.
- 4Develop a SMR for remote deployment and for small grid applications. It has the additional advantage of load-following, process heat application, and improved safeguards features.
- 5Integrate the SMR into a smart grid. The smart grid is a new kind of electric grid, one that is built from the bottom up to handle the groundswell of digital and computerized equipment and technology dependent on it and one that can automate and manage the increasing complexity and needs of electricity in the 21st Century.
Technology Sharing
-
Goal 1
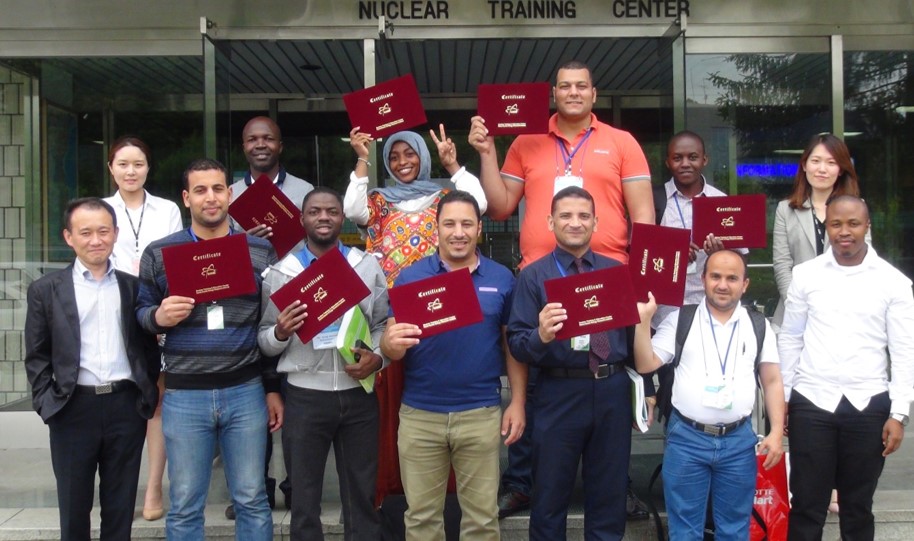 Fostering Practical Engineeringfor Students from Developing Countries
Fostering Practical Engineeringfor Students from Developing Countries- Full scholarship program for students from developing countries
- Internship program for international students
- Accommodations and teaching - aid materials for all students
Strategies- 1. KINGS offer a full scholarship program to international students from various countries ;
- - Middle East : UAE, Yemen, Jordan
- - Africa : Egypt, Nigeria, Kenya, South Africa , Senegal, Uganda, Tanzania, Tunisia
- - Asia : Vietnam, Malaysia, Indonesia, Tajikistan, Mongolia, Bangladesh, Cambodia
- - Europe : Turkey, Romania, Poland
- - South America : Brazil
- 2. KINGS coordinates an internship program for international students during the winter break. Since 2013, Korea Hydro and Nuclear Power(KHNP), Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute(KAERI), and Korea Radioactive Waste Agency(KRWA) have all cooperated with KINGS to give an internship opportunity for international students.
- 3. We also provide single bed rooms in a dormitory to each student. A cooling & heating system, a balcony with a beautiful sea-view, and a bathroom is also available in each room.
-
Goal 2
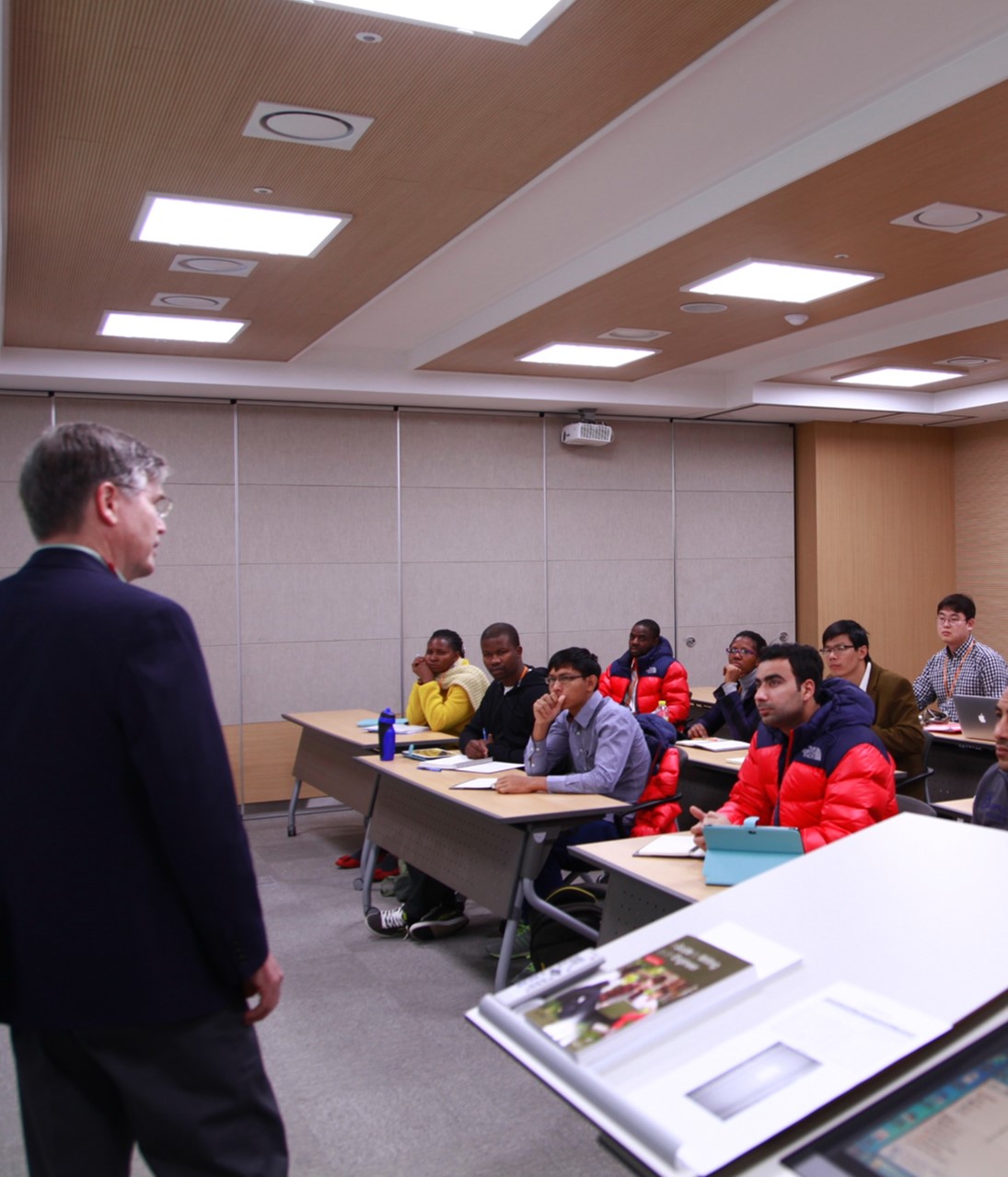 Short-term Non-degree Coursesfor those from Countries Wishing to Introduce Nuclear Power Plants
Short-term Non-degree Coursesfor those from Countries Wishing to Introduce Nuclear Power Plants- IAEA interregional training course
- Short-term training courses for the universities of Middle East and Asian countries
- Short training programs for the officials of the first NPP deploying countries
Strategies- 1. KINGS offers customized short -term training courses for those from countries which are planning to construct their first nuclear power plant or to establish a nuclear engineering department for their university.
- 2. KINGS faculties can be – dispatched to a university requesting special lectures or help for their infant nuclear engineering department.
-
Goal 3
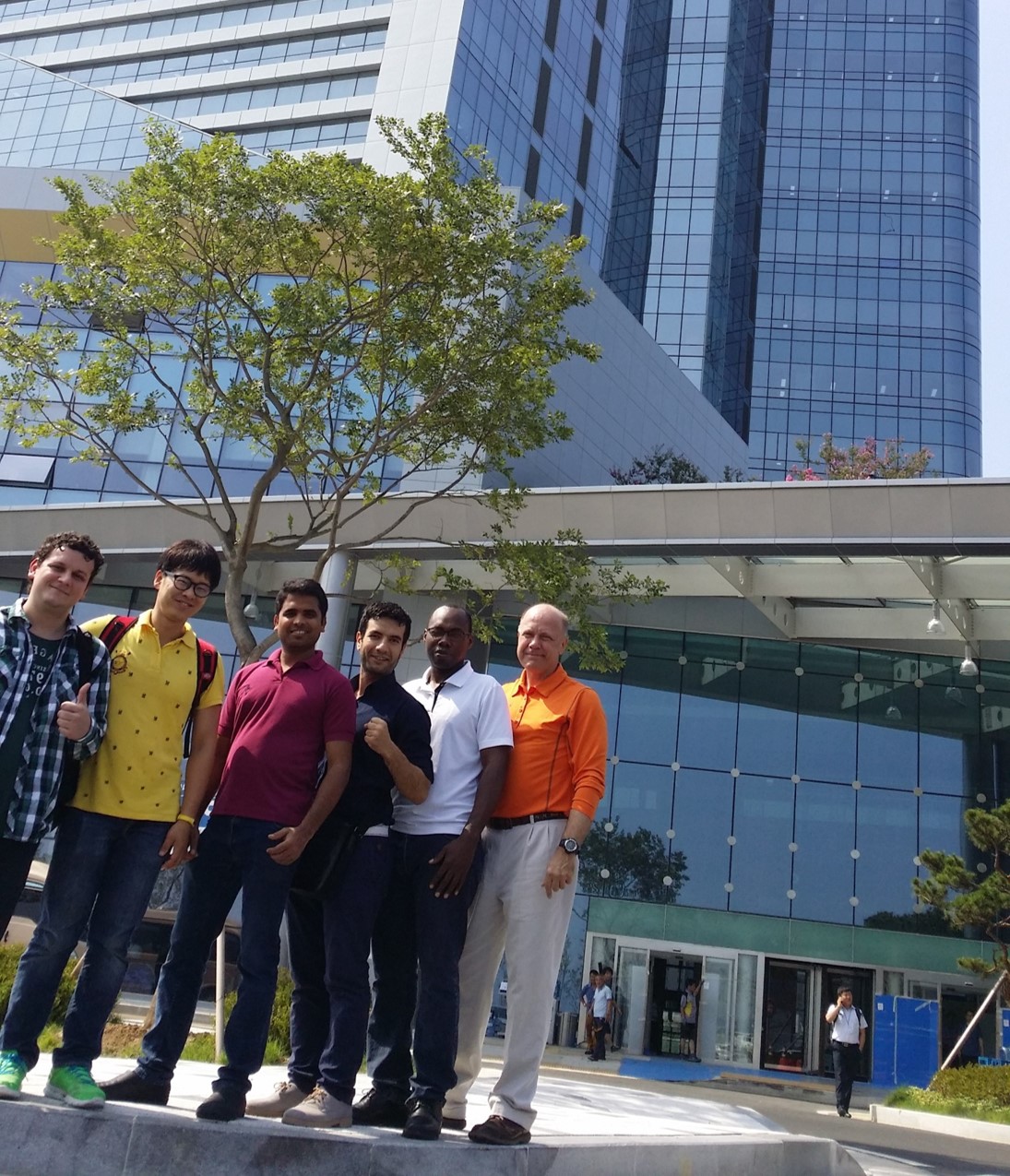 Customized Short Training Coursesfor NPP Industries
Customized Short Training Coursesfor NPP Industries- KHNP Short training courses for NPP engineering
- KEPCO-KPS short training courses for I&C engineers
Strategies- 1. 5- Weeks Senior Expert Course offered to KHNP
- - NPP Power Train and Fluid Mechanics Design
- - NPP Electrical System Design
- - NPP I&C System Design
- - Seismic Analysis and Civil Structure Design
- 2. 8-Weeks I&C Engineer Training Course for KEPCO –KPS
-
Goal 4
 Joint Training with KOICAas an Official Development Assistance ProgramStrategies
Joint Training with KOICAas an Official Development Assistance ProgramStrategies- 1. KINGS and KOICA Joint Training Program for Egyptian Nuclear and Radiological Authority members was performed for 3 weeks in 2015.
- 2. This training course is a capacity development program on safety regulations for nuclear regulators conducted as part of the foreign gratuitous aid projects by KOICA.
- Management :
- Contact :
- Modified date :